Emotional intelligence (EI) is being more recognized as a critical factor in personal and professional success and well being. Understanding and managing your emotions, as well as successfully navigating social difficulties, are all aspects of emotional intelligence. Fortunately, emotional intelligence may be increased through deliberate exercises and practices. Here, we look at three research-backed exercises for improving your emotional intelligence.
Table of Contents
Emotional intelligence 3 exercise
1. Mindful Reflection:
Mindful reflection entails being present with your thoughts and emotions while observing them without judgment. This practice helps you develop insight into your emotional patterns and reactions, which promotes self-awareness.

Why It Works
Mindfulness is linked to increased emotional regulation and empathy. According to research, frequent mindfulness meditation can cause anatomical changes in the brain, including improvements in areas connected to emotional regulation and empathy. Farb et al. (2010) discovered that mindfulness meditation enhanced activity in brain areas related to self-referential processing, resulting in improved emotional awareness and management.
How to Practice?
Set aside time: Set aside 10-15 minutes daily for mindful reflection. Choose peaceful place where you will not be disturbed.
Observe your thoughts: Pay attention to your thoughts and feelings.
Label Your Emotions: As you examine your ideas, try to identify your feelings. Are you experiencing anxiety, excitement, or sadness?
Reflect on Triggers: Consider what could have provoked these emotions. Understanding the causes can help you better control your emotional responses in the future.
Practical Example:
Sarah, a marketing executive, began practicing mindful reflection after becoming overwhelmed with work stress. By observing her thoughts, she discovered a pattern: she was frequently worried before crucial meetings. Identifying this trigger helped her prepare more effectively and control her anxiety, resulting in increased performance and mental well-being.
2. Active Listening:
Active listening entails paying close attention to a speaker, comprehending what they’re saying, responding and reflecting on what they’re saying, and remembering the knowledge for later. This keeps both the listener and the speaker fully involved in the discourse.
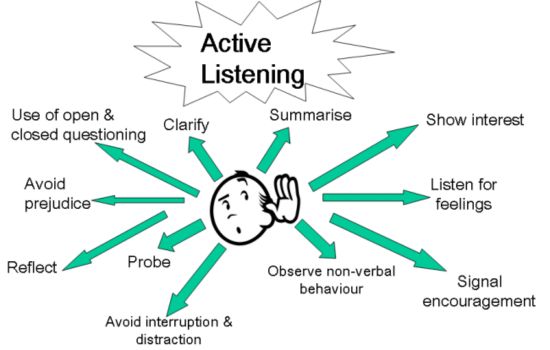
Active listening, reflecting, responding, and providing feedback are not always simple. Here are some useful active listening practices for managers.Pay close attention to the speaker’s actions and body language to acquire a deeper grasp of their message.Visual indicators such as nodding and eye contact can indicate that you’re paying attention; ask clarifying questions to guarantee your understanding.
Why it works:
Weger et al. (2014) found that active listening increases relationship satisfaction and communication effectiveness. Understanding others’ viewpoints and feelings allows you to respond more empathetically and constructively.
How To Practice:
Give Full Attention: When someone speaks, give them your full attention. Remove any distractions, such as phones or laptops.
Use non-verbal cues. Use body language. Nod, which is make eye contact, and lean slightly forwards.
Reflect and Clarify: Ask clarifying questions as needed.
Respond Thoughtfully: When responding, consider what you’ve heard and not just your own opinions.
Practical Example:
In a practical example, John, a team leader, observed low engagement during meetings. His team felt more respected and understood, resulting in increased team cohesion and efficiency.
3. Emotional Journaling:
Write down your thoughts on regular basis.This activity can help you process your emotions, recognize trends, and gain a better understanding of yourself.

Why It Works:
Writing in a journal facilitates the externalization of your inner experiences, which facilitates comprehension and management.It aids in mental clarity, stress reduction, and mood enhancement.
How To Practice:
Set a routine: Set up a consistent time each day to write in your journal, such as before bed or after waking up.
Write freely. Concentrate on your feelings and experiences. Please don’t worry about grammar or spelling. The point is that to express honestly.
Identify patterns. Review your entries over time to see if there are any repeating themes or emotional triggers.
Reflect on Growth: Use a writing book to track your emotional development and understand how to react to situation change.
Practical Example:
Emma, a student dealing with anxiety, started journaling about her daily experiences. Writing about her fears allowed her to spot trends and triggers, such as upcoming exams or social gatherings. She gradually acquired coping methods to better manage her anxiousness.
Conclusion:
Developing emotional intelligence requires ongoing study and practice. Mindful reflection, active listening, and emotional journaling are three useful exercises for increasing emotional awareness, empathy, and self-regulation. By implementing these techniques into your daily routine, you may strengthen your relationships, increase your mental well-being, and face life’s obstacles with greater resilience.

